The Bell Eagle Eye is a tiltrotor unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) developed by Bell Helicopter, a unit of Textron. The Eagle Eye is the most versatile vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL), integrating advanced technology in a reliable platform to demonstrate mission effectiveness.
The first Eagle Eye demonstrator UAV model, TR-911X, completed its first flight in March 1998. The UAV reached a maximum speed of 200kt and flew to an altitude of 14,000ft, while carrying an operational payload of around 98kg.
Eagle Eye tiltrotor UAV design
The UAV design incorporates a tiltrotor configuration with two rotor systems and transmission nacelles on each wing tip. The airframe includes forward fuselage, centre fuselage, aft fuselage, wings and pylons. The vehicle operates as a helicopter during the take-off and landing, but the nacelles rotate 90 degrees forward to convert the aircraft into a turboprop during flight.
The mechanically synchronised rotor system is powered by a single engine located in the centre fuselage section. The pylon structure includes upper and lower halves. The composite wing structure consists of forward and aft spar, lower and upper laminates. The single-piece composite elements attached to the wing are flaperons.
Eagle Eye UAV missions
The Bell Eagle Eye UAV was developed to conduct intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance missions in land-based or sea-based environments. It can be deployed in range of unmanned aerial missions including border patrol, NBC detection, real-time situational awareness for tactical forces, target identification, electronic countermeasures, airborne radio relay, fisheries protection and fire detection.
Additionall, the UAV can act as a guidance system for naval or artillery gunfire, attack helicopters, airstrikes and extended-range munitions, and deliver sonobuoys in anti-submarine warfare operations.
Avionics
The avionics suite consists of flight control system, flight control computer, air data computer, radio altimeter, IFF transponder, UAV common automatic recovery system transponder, decklock device, airborne data link terminal, electrical power system and payload interfaces. Communications are provided by VHF/UHF radio. The flight control system integrates redundant sensors, processing elements, drive electronics, monitoring, wiring, actuator motors and data links.
Fuselage
The fuselage section is divided in to three parts: forward, centre and aft. The forward fuselage can accommodate modular payloads and is fitted with support beams and mounted adapter plates to hold the payload. The centre fuselage section includes aircraft propulsion system, landing gear, fuel system, air management system and flight control system. The horizontal and vertical stabilisers are fitted on the aft fuselage section. This section also houses the navigation equipment.
Navigation and communication
The UAV can be controlled through the UAV common automatic recovery system, which integrates an airborne subsystem consisting of the omnidirectional and directional antennas.
Sensors and radars
The sensor suite includes a navigation sensor, an ice detection sensor, fuel sensors, and engine and transmission sensors. The UAV is also equipped with a RDR-1700 multi-mode radar developed by Telephonics Corporation. Though primarily designed for airborne search and surveillance operations, the radar can also be used for terrain mapping, weather avoidance, beacon detection and oil slick detection.
The UAV is also equipped with SAFIRE III airborne thermal imaging system. The system comprises micro-scanned detector and a three field-of-view colour spotter scope with haze penetration filter.
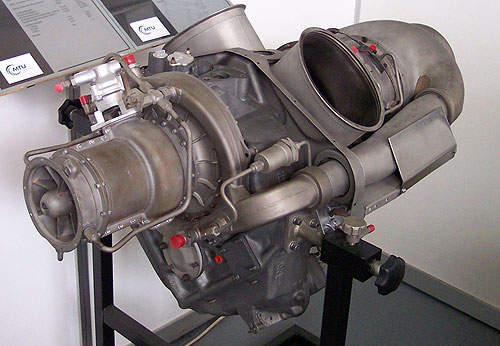
Engines
Eagle Eye is powered by a Pratt & Whitney PW 200/55 turboshaft engine. Designed to operate in a maritime environment, the engine can provide a five minute take-off rating of 641shp. The UAV also has two proprotors.
Landing gear
The Eagle Eye is fitted with a retractable dual-wheel tandem landing gear with outriggers mounted on the centre fuselage. The independent gas / oil struts are installed on four points to absorb landing loads. The outriggers are attached to pylon gearboxes and tilt forward during flight. The UAV is also equipped with the deck arrest system.
Ground control station
The UAV’s ground control station is equipped with air vehicle command and control software and dual redundant architecture. The primary links system uses the tactical common data link technology. The external data link component includes a forward primary antenna, aft primary antenna and secondary antennas. The data link transmits the real-time colour video, radar and voice data.
Performance
The Eagle Eye UAV can fly at the speed of over 200kt, and can cover 800nm between take-off and landing locations. The altitude of the UAV is limited to 20,000ft based on the mission requirements. The vehicle has approximately six hours of total endurance with 90.7kg of payload.