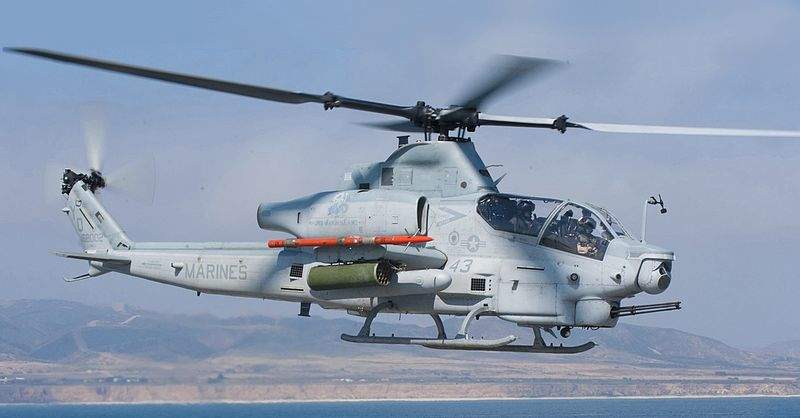
The US Navy has successfully completed its first joint air-to-ground missile (JAGM) flight test on the AH-1Z helicopter at Naval Air Station Patuxent River.
The aircrew navigated the missile through a wide range of operational modes in order to demonstrate its compatibility with the helicopter and exercised its active seeker to search and / or acquire targets.
JAGM Flight Test lead Liam Cosgrove said: “Initial results from the flight indicate the missile performed as planned.
“We will continue to conduct a series of tests to prepare for live-fire testing of the JAGM off the AH-1Z scheduled for early this year.”
The JAGM is a precision-guided missile that can be used against high-value stationary, moving and relocatable land and maritime targets.
It is being collaboratively developed by the US Navy and the US Army.
How well do you really know your competitors?
Access the most comprehensive Company Profiles on the market, powered by GlobalData. Save hours of research. Gain competitive edge.

Thank you!
Your download email will arrive shortly
Not ready to buy yet? Download a free sample
We are confident about the unique quality of our Company Profiles. However, we want you to make the most beneficial decision for your business, so we offer a free sample that you can download by submitting the below form
By GlobalDataThe missile uses a multi-mode seeker to provide targeting day or night in adverse weather and battlefield obscured conditions, as well as against a wide range of countermeasures.
The JAGM munition is managed by the Program Executive Office for Missiles and Space in Redstone Arsenal, Alabama, and is initially set to be integrated on-board the AH-64 Apache and US Marine Corps’ AH-1Z helicopters.
JAGM is also compatible with any aircraft that can support the installation of Hellfire missiles.
Naval Air Systems Command (NAVAIR) Direct and Time Sensitive Strike (PMA-242) programme manager captain Mitch Commerford said: “This missile will provide increased lethality and better targeting capabilities beyond the Hellfire’s laser point designating capability that the AH-1Z currently has in theatre today.”
The US Army is scheduled to complete a 48-shot test matrix on the AH-64 Apache helicopter in support of Milestone C during the first half of this year.