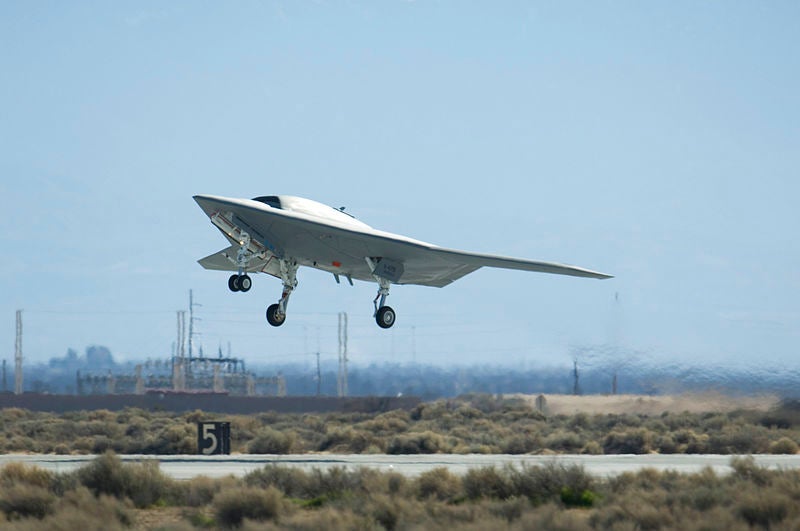
The US Navy and Northrop Grumman have successfully completed a series of flight tests of the ship-based X-47B unmanned air vehicle (UAV) technology in St. Augustine, Florida, US, as part of the US Navy’s UCAS-D programme to create a carrier-based unmanned aircraft.
During the demonstration, the aircraft was tested using both boom/receptacle and probe-and-drogue aerial refuelling techniques but no fuel was actually exchanged between the other aircraft involved.
Northrop Grumman’s UCAS-D AAR programme manager, Pablo Gonzalez, said that the recent flight test validated the X-47B’s ability to conduct aerial refuelling operations with accuracy and precision.
Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems sector vice president and UCAS-D programme manager Carl Johnson said the tests ensure autonomous aerial refuelling (AAR) using either the Navy’s probe-and-drogue refuelling technique or the US Air Force’s boom/receptacle approach.
‘Future unmanned systems will need to use both refuelling techniques if they plan to conduct longer range surveillance or strike missions from the carrier’, Carl Johnson added.
The specially equipped variable stability Lear jet was used as a stand-in for the demonstrator aircraft, while a K707 tanker with a Navy refuelling drogue was used to simulate the fuel transfer procedure.
The X-47B is a tailless unmanned combat aircraft with low-visibility, featuring a hybrid GPS/vision-based relative navigation system and autonomous flight control system to maintain a precise distance between the tanker and receiver aircraft.
The aircraft will undergo additional AAR surrogate testing, with other aircraft using flight-qualified versions of the relevant X-47B hardware and software.
Additionally, the X-47B aircraft capability to launch from a carrier, recovery, bolter and wave-off performance will be validated next year.
Northrop is the US Navy prime contractor for the unmanned combat air system demonstration (UCAS-D) programme awarded in 2007 to design, develop and produce two X-47B aircraft for the US Navy.
The autonomous aerial refuelling demonstrations are planned for 2014.
Image: US Navy and Northrop complete a series of flight tests of the ship-based X-47B unmanned air vehicle (UAV) technology. Photo: Rob Densmore.