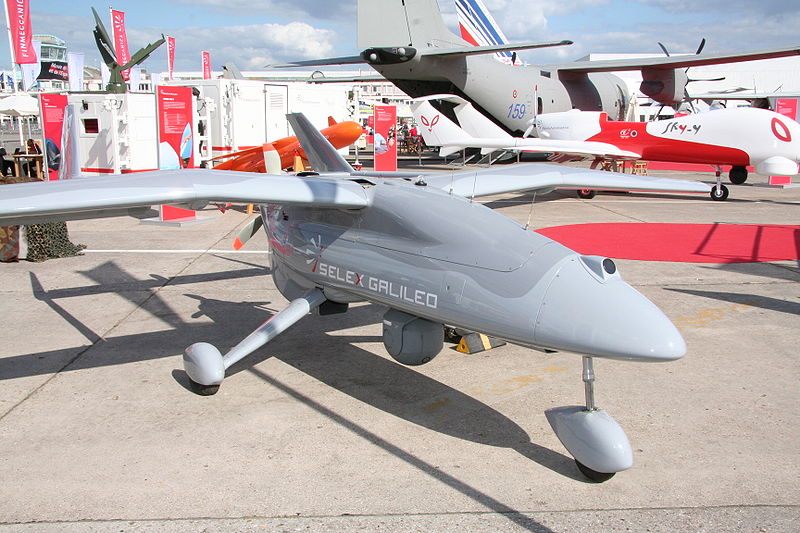
Selex ES’s Gabbiano T-20 radar has successfully demonstrated ground-mapping and target detection capabilities onboard a Falco unmanned aircraft system (UAS) in Bulgaria.
The testing was designed to validate the radar’s high-resolution ground mapping, with both strip and spot synthetic aperture radar (SAR), as well as air-to-sea surveillance with track-while-scan (TWS) modes.
The radar also proved its ship-target imaging and classification with inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR) mode and navigation with ground-mapping and weather avoidance, while enhancing Falco’s long-range surveillance capabilities.
Commenting on the trials, Selex ES unmanned aerial systems head Fabio Pauluzzo said: "The successful combination of our Falco and Gabbiano product families will allow Selex ES to provide a more versatile tactical UAV solution for typical MALE multi-sensor missions."
Selex airborne and space systems division marketing and sales director Fabrizio Boggiani was quoted by Shephard as saying: "Having successfully integrated the Gabbiano, we can now offer the Falco with a multi-mode radar, allowing the platform to perform missions that require land, sea and coastal surveillance."
The lightweight, easy-to-install Gabbiano T-20 radar has been designed for conducting short or long surveillance missions in all weather conditions.
Capable of operating onboard unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV), as well as both fixed and rotary wing manned aircraft, the radar helps perform combat search-and-rescue (SAR) and covert operations of Special Forces by day or night.
In addition, Gabbiano radar features dual channel digital receiver and standard and flexible interfaces to support maritime patrolling and SAR operations.
Selex Galileo-built Falco medium-altitude endurance UAS supports reconnaissance and surveillance missions using its integrated thermal imager, a spotter or a laser designator, nuclear, biological and chemical (NBC) sensor, electro optic (EO) sensor and an infrared (IR) sensor.
Image: Falco unmanned vehicle takes off. Photo: file image.