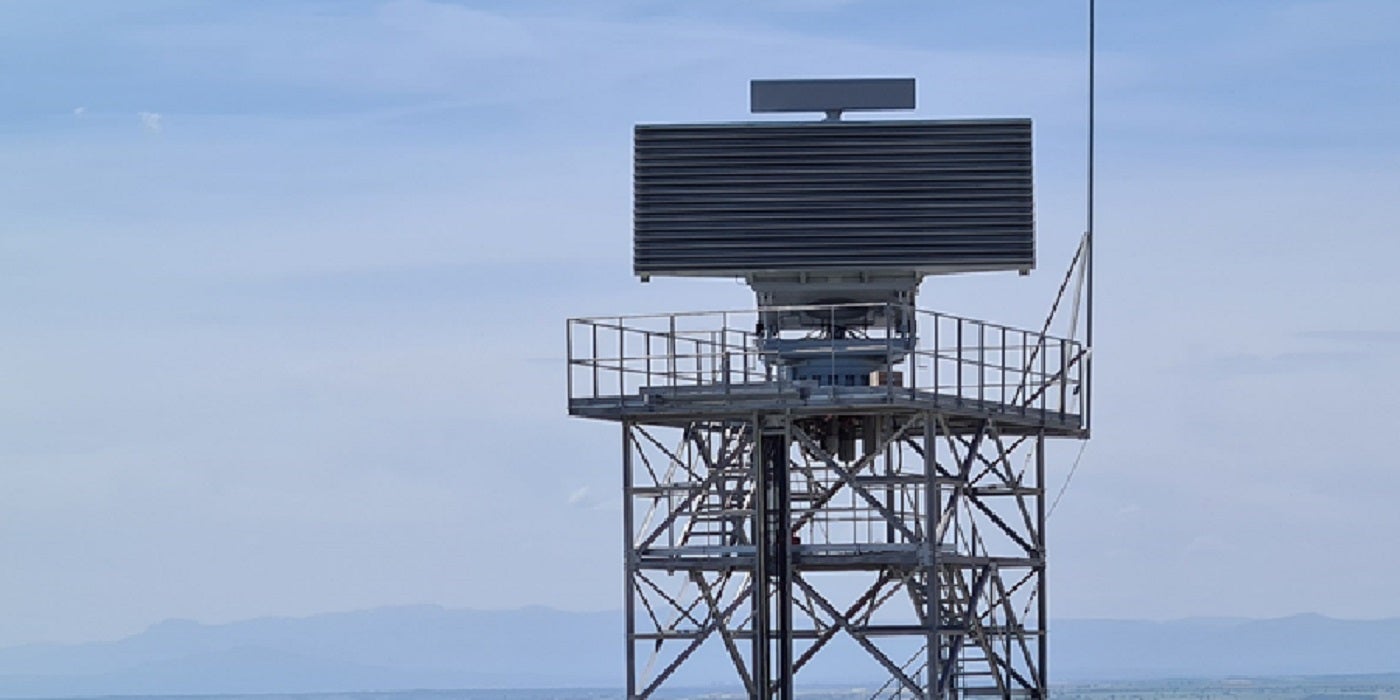
Indra has installed the first of the 23 Lanza-N radars that will equip Indian Navy ships over the next decade.
The Madrid-based tech company are the original equipment manufacturer of the 3D radar system. The Lanza radars will replace the ELM-2248 MF-STAR and RAWL-02/LW-08 radars on India’s destoryers: Kolkata-class and Visakhapatnam-class, according to GlobalData Defence analyst Tushar Mangure.

Discover B2B Marketing That Performs
Combine business intelligence and editorial excellence to reach engaged professionals across 36 leading media platforms.
Indra and the Hyderabadi defence company, TATA Advanced Systems, signed a deal in 2020 as part of a technology transfer programme.
Indra has adapted the Lanza-N radar – based on the one installed in the Spanish ship Juan Carlos I – to the regulatory requirements of India. The modifications suit Indian Ocean conditions, guaranteeing optimum performance in high humidity and extreme heat conditions.
The Lanza family are multi-scenario, multi-threat adaptive radars. The radar design operates according to Nato’s technical requirements and it anticipates the changing threat scenario of the future.
The Lanza-N integrates a 3D primary surveillance radar that provides medium and long range coverage up to 254 nautical miles. The radar detects aircrafts, even under adverse conditions, including clutter. Target co-ordinates provided by the surveillance radar include target altitude (3D position).
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataIndia’s plans for Lanza-N
GlobalData intelligence tells us that the Indian Navy plans to integrate the radar more widely.
“The Lanza-N radar system may also be deployed onboard the Nilgiri-class frigates, which are already in advanced stages of construction.
“There is a strong possibility that these radars will also be installed on the Navy’s future Project-18 Next-Generation Destroyer. Moreover, the acquisition of the new radar is also in line with the navy’s Maritime Capability Perspective Plan (MCPP), which places a priority on expanding the capabilities of naval platforms in addition to increasing fleet size numerically,” Mangure adds.
Currently, the Indian Ministry of Defence claims its present force level comprises 150 ships and submarines. India’s perspective-planning moves from the number of platforms to one that concentrates upon its capabilities.
This is a common naval strategy in the current security climate. Navies are producing less costly vessels more quickly – such as the Indian navy’s Niligiri-class frigates, the US Navy’s littoral combat ships, or the increased operations of the UK Royal Navy’s patrol vessels HMS Spey and HMS Tamar in the Indo-Pacific.